Vision plays a vital role in how we experience the world, from reading and working to driving and enjoying everyday activities. In today’s screen-heavy, fast-paced lifestyle, the role of an optometrist in modern eye care has expanded well beyond simply prescribing glasses. Optometrists are primary eye care professionals who help maintain, protect, and improve vision while also detecting early signs of eye diseases and broader health issues.
What Is an Optometrist?
An optometrist is a licensed healthcare professional trained to examine, diagnose, manage, and treat a wide range of vision and eye health conditions. Unlike ophthalmologists, who are medical doctors and perform eye surgery, optometrists focus on comprehensive eye care, vision correction, and early disease detection.
The role of an optometrist sits at the frontline of eye health. They are often the first professional to identify changes in vision or signs of underlying health conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, or neurological disorders.
The Role of an Optometrist in Eye Examinations
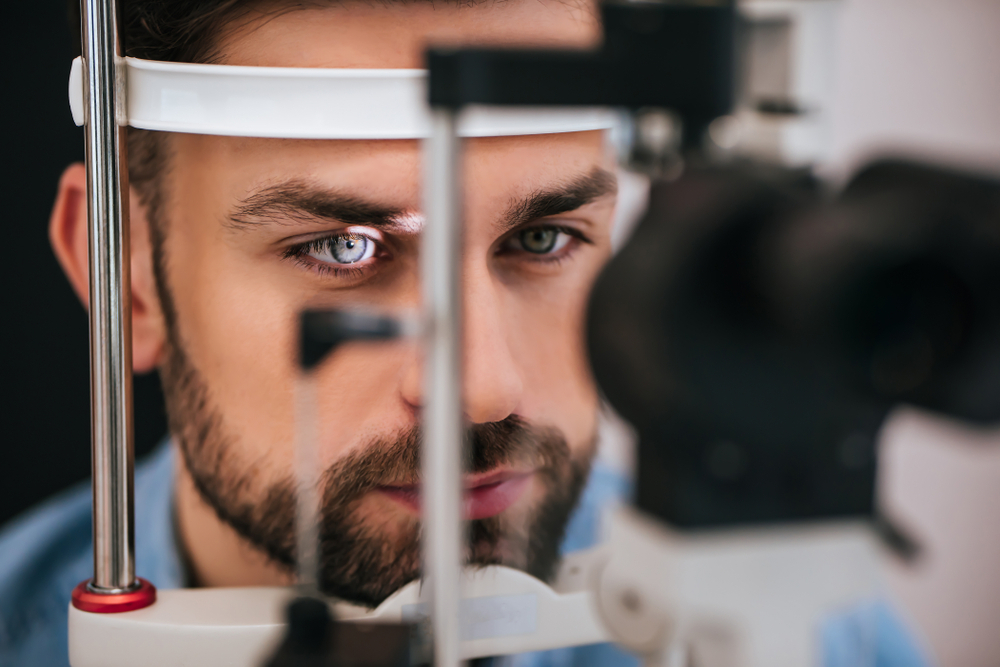
One of the primary responsibilities in the role of an optometrist is conducting thorough eye examinations. These assessments go far beyond reading letters on a chart. A comprehensive eye exam includes:
- Measuring visual acuity
- Assessing eye coordination and focusing ability
- Checking peripheral (side) vision
- Evaluating eye pressure
- Examining the retina and optic nerve
Through these tests, optometrists can detect early signs of conditions such as glaucoma, macular degeneration, cataracts, and retinal diseases often before symptoms become noticeable.
Vision Correction and Prescription Services
Another core aspect of the role of an optometrist is prescribing vision correction solutions. This includes:
- Glasses for near, distance, or multifocal vision
- Contact lenses, including specialised and therapeutic lenses
- Myopia (short-sightedness) control strategies for children
Optometrists carefully assess lifestyle needs when recommending vision correction. Whether a patient works on a computer all day, plays sports, or drives frequently at night, optometrists tailor prescriptions to enhance comfort and clarity in daily life.
Early Detection of Eye Diseases
The role of an optometrist is critical in identifying eye diseases at an early stage. Many serious eye conditions develop gradually and without pain, making routine eye exams essential.
Optometrists are trained to detect and manage conditions such as:
- Glaucoma
- Diabetic retinopathy
- Age-related macular degeneration
- Dry eye disease
- Keratoconus
Early diagnosis allows for timely referral to ophthalmologists when necessary, preventing vision loss and preserving long-term eye health.
Managing Digital Eye Strain and Modern Vision Problems
With increased screen time from computers, smartphones, and tablets, digital eye strain has become a common concern. The role of an optometrist now includes helping patients manage modern vision challenges caused by prolonged device use.
Optometrists may recommend:
- Specialised computer or blue-light filtering lenses
- Ergonomic advice for screen use
- Dry eye treatments related to reduced blinking
- Visual therapy exercises
These solutions help reduce symptoms such as headaches, blurred vision, eye fatigue, and dryness.
Children’s Vision Care and Development
The role of an optometrist is especially important during childhood, as vision development plays a crucial role in learning and overall growth. Undiagnosed vision issues can affect reading, concentration, and academic performance.
Optometrists assess:
- Eye alignment and coordination
- Focusing ability
- Myopia progression
- Visual perception skills
Early intervention can correct or manage issues before they impact a child’s education and confidence. Many optometrists also provide myopia control programs to slow the progression of short-sightedness in children.
The Role of an Optometrist in Overall Health Monitoring
Eye examinations can reveal more than just vision problems. The role of an optometrist often overlaps with general health monitoring, as the eyes provide valuable insight into the body’s overall condition.
During an eye exam, optometrists may identify signs of:
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Autoimmune conditions
- Neurological disorders
This early detection allows patients to seek timely medical care, reinforcing the optometrist’s role as a key part of the healthcare system.
Why Regular Eye Exams Matter
Understanding the role of an optometrist highlights why regular eye exams are essential—even when vision seems fine. Many eye conditions develop silently, and early detection is the key to preserving sight.
Most adults should have an eye exam every one to two years, while children, seniors, and individuals with existing eye or health conditions may need more frequent visits.
Conclusion
The role of an optometrist extends far beyond prescribing glasses. Optometrists are trusted primary eye care professionals who play a crucial role in vision correction, disease detection, preventive care, and overall health monitoring. From children to seniors, their expertise supports clear vision, eye health, and quality of life at every stage.









Leave a Review