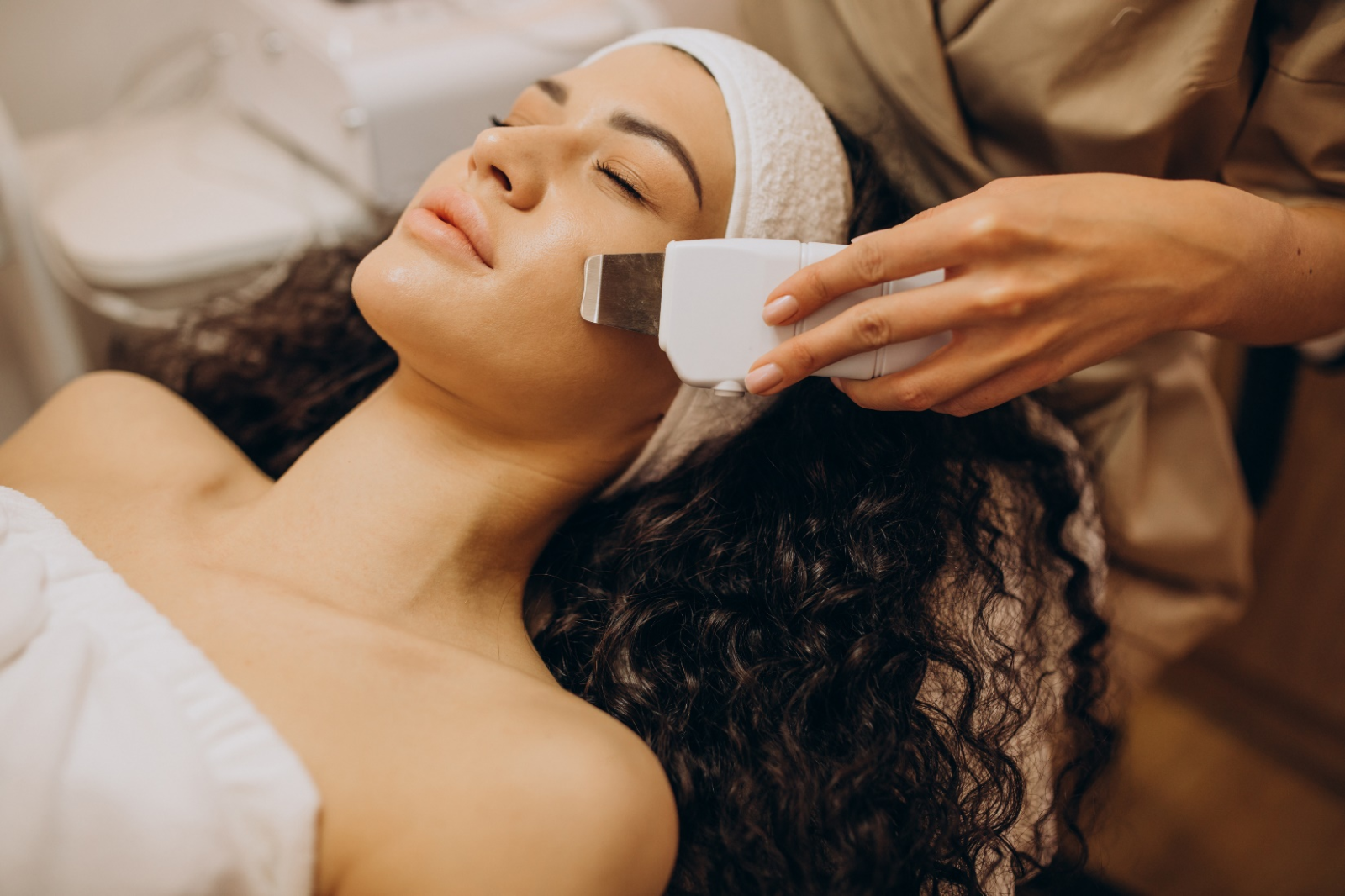
In dermatology, skin hyperpigmentation is a condition in which the colour of the skin changes, causing it to become discoloured or darker in appearance. In other cases, it takes a long time for treatments to show results, and patients may not adhere to their regimens. Pigmentation treatment is something people are always in lookout for, because who doesn’t want to look good and feel beautiful. Consequently, people can experiment with various therapeutic approaches, including at-home therapies, as a result.
What do you think the phrase “hyperpigmentation” refers to exactly?
When the skin generates more melanin than it needs to keep up with the body’s demands, skin flaws or darker skin sections in hue than the surrounding areas would look darker. Hyperpigmentation of the skin is a skin disorder that affects many people worldwide and people opt for Pigmentation treatment. Individuals of all skin tones are affected by this condition. The face, arms, and legs are among the most common areas of the body where hyperpigmentation can occur. Melasma and sunspots are among the most common types of hyperpigmentation. Cuts, burns, acne, and lupus can result in hyperpigmentation, depending on where the body is located.
What is the best way to get rid of hyperpigmentation?
Although hyperpigmentation is not harmful, some people would prefer to be free of the condition altogether. The following measures should be implemented to prevent or slow the progression of hyperpigmentation:
- To protect the skin and prevent hyperpigmentation from becoming more evident over time, use sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher.
- A person should try to avoid picking at their skin, if at all. However, when it comes to scratching at patches, scabs, and acne, you should avoid doing so to prevent hyperpigmentation after an injury.
- According to the distribution and extent of skin involvement, treatment options include topical corticosteroids, if the melanocytes is stable and self-limiting, patients may be candidates for surgical grafting operations.
- Still, those with more severe illnesses may be candidates for Pigmentation treatmentto enhance skin tone.
The Factors That Contribute to Hyperpigmentation
The type of hyperpigmentation determines the cause of hyperpigmentation. The following are the most common factors that contribute to hyperpigmentation:
- Exposure to sunlight
The body produces more melanin to protect the skin from prolonged exposure to the sun. This may result in the development of age spots or sunspots and dark spots or patches on the skin. Pigmentation treatment is easy for this case because such discolorations are temporary.
- Skin inflammation
After a person’s skin has been irritated, skin regions can become discoloured. Acne, eczema, lupus, or a skin injury are examples of skin conditions. Additionally, persons with darker skin are more likely than others to develop post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
- Melasma
When a person’s hormone levels fluctuate, darker patches of skin may emerge. In women who are pregnant, this type of hyperpigmentation is quite common. Extra pigmentation in certain skin places is usually innocuous, though it may occasionally indicate the presence of another medical disease.
- Reactions to prescription medications
Antimalarial medications and tricyclic antidepressants, for example, have been shown to cause hyperpigmentation in some patients. Skin discoloration can occur in patches on the body in certain circumstances. Chemicals used in topical treatments have the potential to cause hyperpigmentation as well.
Pigmentation treatment has limitations and adverse effects such as erythema, skin peeling, and dryness, and they require a significant amount of treatment time to provide noticeable improvements. Because of the limitations of present treatments, additional research is needed into emerging approaches to treating hyperpigmentation. New therapy formulations are being investigated, such as solid lipid Nano carriers and liposomes and phytochemicals, platelet-rich plasma, and micro needling






Find Us on Socials